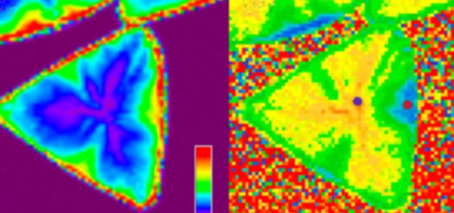
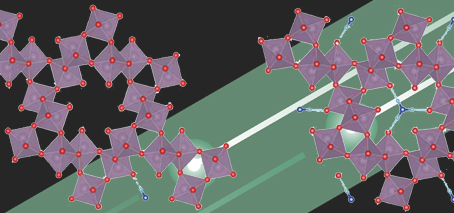
Molecular self-assembly on a metal results in high-density 2D organic (carbon-based) quantum dot array with electric-field-controllable charge state Organic molecules used as nano-sized building blocks in fabrication of functional nanomaterials The achieved densities of the 2D organic quantum-dot arrays are an order of magnitude larger than conventional inorganic systems. A Monash University experimental study has fabricated a self-assembled, carbon-based nanofilm …
UNSW student focuses kilometre-long laser
UNSW PhD student focuses one-km long laser to probe electronic structure Measuring femto-second responses on X-ray Free Electron Laser (XFEL) One of the highest energies of any synchrotron in the world. “It’s a pretty surreal being at the pointy end of almost a kilometre-long laser,” says UNSW PhD student Oliver Paull. “Not because of any danger from the laser (even …
Recognition of hard work, PhD submitted – congratulations Stuart Burns, UNSW
Congratulations to FLEET PhD student Stuart Burns, who submitted his PhD thesis recently, and whose hard work was rewarded by a rare UNSW scholarship to continue to carry out research while his thesis is being reviewed. Stuart is a PhD candidate working with Prof Nagy Valanoor and Dr Daniel Sando at UNSW to study the functional behaviours of ferroelectrics at …
Impossibly cool: Negative absolute temperatures
—by Dr Shaun Johnstone (Monash University) and Dr Tapio Simula (Swinburne University of Technology) One of the first things we learn about the absolute temperature scale, measured in degrees Kelvin, is that it’s impossible to get temperatures below Absolute Zero. But in a recent pair of FLEET studies into turbulence, researchers were working in a regime of precisely that: negative …
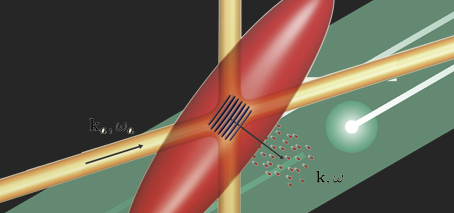
Experimental observation of a new class of materials: excitonic insulators
First observation of excitonic insulator New exotic state was first predicted in 1960s A University of Wollongong / Monash University collaboration has found evidence of a new phase of matter predicted in the 1960s: the excitonic insulator. The unique signatures of an excitonic insulating phase were observed in antimony Sb(110) nanoflakes. The findings provide a novel strategy to search for …
AI Yuerui Lu recognised by Heart Foundation
FLEET Associate Investigator Professor Yuerui Lu (ANU) has been named a Heart Foundation Future Leader Fellow. The innovation of Professor Lu’s research, which focuses on the next-generation high-throughput 3D microscopy for cardiovascular imaging, was also recognised by the Foundation’s Paul Korner Innovation Award. This project aims to demonstrate proof of the concept for a novel high-throughput 3D microscope using ultra-thin, …
Lights out: Putting the ambient air oxidation of Monolayer WS2 to bed
Oxidation of monolayer WS2 in ambient requires exposure to light, and keeping samples in darkness can protect from oxidation Routine exposure to room lights (days) or light microscopes can cause significant oxidation, suggesting wide reaching implications for current and future studies of monolayer S-TMDs To protect monolayer semiconductor transition metal dichalcogenides (S-TMDs) from oxidation, they must be entirely shielded from …
Women in FLEET Fellowships
FLEET’s goal is to achieve 30% representation of women at all levels across FLEET. To begin to move towards this goal, we needed innovative approaches that would allow us to begin ‘shifting the dial’. One innovative initiative that has met with success was FLEET’s new women-only Fellowships, offered in multiple locations, and across all fields of study in the Centre. …
First observation of native ferroelectric metal
In a paper released today in Science Advances, UNSW researchers describe the first observation of a native ferroelectric metal. The study represents the first example of a native metal with bistable and electrically switchable spontaneous polarization states – the hallmark of ferroelectricity. “We found coexistence of native metallicity and ferroelectricity in bulk crystalline tungsten ditelluride (WTe2) at room temperature,” explains …
Collaboration unlocks new magnetic properties for future, faster, low-energy spintronics
• RMIT–UNSW collaboration combines theory, experimental expertise • ‘Spintronic’ applications promise faster, more efficient computing • New magnetic properties of 2D Fe3GeTe2 (FGT) discovered A theoretical–experimental collaboration across two FLEET nodes has discovered new magnetic properties within 2D structures, with exciting potential for researchers in the emerging field of ‘spintronics’. Spintronic devices use a quantum property known as ‘spin’, in …
Meet molybdenum, an acid-free route to future Hydrogen power?
Molybdenum based compounds could provide key to hydrogen production for future zero-emissions energy RMIT/Monash collaboration opens promising route towards alkaline hydrogen production A FLEET study combining experimental expertise at RMIT with theoretical modelling at Monash University opens a new route towards efficient, cost-effective production of hydrogen. Researchers discovered that ammonium-doped, hexagonal molybdenum oxide (MoO3) displays extremely promising electronic and material …
Order from chaos: Australian vortex studies are first proof of decades-old theory
Seminal, seventy-year-old theory of turbulence experimentally verified for first time Applications range from Jupiter’s Great Red Spot to electron movement in superconductors Images and video available Two Australian studies published this week offer the first proof of a 70-year-old theory of turbulence. “The studies confirm a seminal theory of the formation of large-scale vortices from turbulence in 2D fluid flow, …
Using disorder to build new materials for low-energy electronics: welcome new FLEET AI Julie Karel
Dr Julie Karel conducts research at the intersection of materials science and condensed matter physics to develop new materials for emerging low-energy nanoelectronic and magnetoelectronic devices. Originally from the US, Julie developed new thermal interface materials to improve mobile-device performance at Intel, and was a postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute in Germany. In materials design, Julie uses complete …
Tuning the topological insulator Sb2Te3: just add iron
Iron-doping of the topological insulator Sb2Te3 results in useful electronic and magnetic properties, quantified in a recent FLEET study at the University of Wollongong. The researchers studied the magneto-transport properties of an iron-doped topological insulator (Fe–Sb2Te3). After the material is doped via the addition of iron, its electronic structure changes significantly: multiple response frequencies emerge, in contrast to the single …
Ultra-cold lithium atoms shed light on pair formation in superfluids, helping identify best theories
• Abrupt onset of pairing points to best theories for describing ultra-cold ‘Fermi gases’ • Implications for understanding of superconductors, superfluids in future ultra low-energy electronic systems A FLEET/Swinburne study released this week resolves a long-standing debate about what happens at the microscopic level when matter transitions into a superconducting or superfluid state. Correlations between pairs of atoms in an …
Deciphering the fundamental physics of ferroelectricity at the nanoscale
Welcome new AI Laurent Bellaiche Welcome to Prof Laurent Bellaiche, whose ongoing research collaborations with FLEET are recognised by him becoming a Centre Scientific Associate Investigator. At the University of Arkansas (US), Prof Bellaiche leads first-principles-based theoretical studies of ferroelectrics, magnetic compounds, multiferroics and other semiconductors. He has co-authored over 310 refereed journal articles, his publications have been cited more …
New Josephson junction study links quantum theory to experiment
The Josephson junction is one of the most important elements in turning quantum phenomena into usable technology. A new RMIT study establishes a theoretical framework for new optical experimentation on these key devices, with implications for future fundamental quantum research and applications such as quantum computing. Josephson junction studies Josephson junctions can be formed by two superconducting plates, separated by …
Topological physics finds Famelab success
Congratulations to FLEET’s Sam Bladwell (right, UNSW), who won the NSW semifinal of Famelab, talking about study of electron spin, and will now compete in the finals in Perth on May 8th. Topological physics has done particularly well in this year’s Famelab, with FLEET associates Dr Semonti Bhattacharyya and Dr Antonija Grubisic-Cabo (Monash University) also qualifying for the Victorian semifinals. …
Welcoming two new Associate Investigators
Dr Dmitry Efimkin (right) is a Scientific Associate Investigator at Monash University specialising in novel materials such as Dirac materials, graphene and topological insulators, and optical phenomena in solids. Within FLEET, Dmitry works with CIs Michael Fuhrer, Meera Parish, and Nikhil Medhekar in Research theme 2: exciton superfluids and Enabling technology A: atomically-thin materials, studying optical and collective phenomena in …
FLEET collaboration reviews ferromagnetism in 2D materials
* Two-dimensional magnetism reviewed in new, collaborative review A collaborative FLEET study has reviewed recent progress in 2D ferromagnetism, and predict new, possible 2D ferromagnetic materials. The study also introduces possible applications of atomically-thin ferromagnets in novel dissipationless electronics, spintronics, and other conventional magnetic technologies. The scientists propose a new method of observing 2D ferromagnetism that could reveal new materials. …
I can’t believe it’s not graphene: nanoengineering artificial graphene
New facility improves study of ‘artificial graphene’ at FLEET ‘Like driving a new Maserati!’ The amazing electrical properties of graphene and other 2D, atomically-thin crystals are due to the symmetry of their lattice structure. For example, it is graphene’s famous ‘honeycomb’ lattice that causes electrons to act as they were massless – moving about 70 times faster than in silicon …
Meera Parish named APS 2019 Outstanding Referee
FLEET’s Meera Parish has been named 2019 Outstanding Referee, the only one in Australia, by the influential American Physical Society (APS). The APS selected 143 Outstanding Referees for 2019, each of whom have demonstrated exceptional work in the assessment of manuscripts submitted to the Physical Review journals. The Outstanding Referee program recognises approximately 150 currently active referees each year, and …
Topological defects could be key to future nano-electronics
• Ferroic and multiferroic topological structures offer exciting potential in future nanoelectronics • Commentary piece published this week in Nature Materials The connection from fridge magnets to cutting edge materials science is shorter than what one might expect. The reason why a magnet sticks to your fridge is that electronic spins or magnetic moments in the magnetic material spontaneously align …
Networking and skills development: Canberra Summer School
Recognising the increasing importance of topological physics, FLEET helped run the 2018 Canberra International Physics Summer School on Topological Matter at ANU – a great opportunity for early-career Australian physicists to hear from leading experts from around the world. Over 90 attendees discovered topological materials’ applications to photonics, ultra-cold systems and quantum computation. Nobel laureate Prof Duncan Haldane (Princeton University) …
Expanded partnership with Tsinghua University: meet FLEET’s two new Partner Investigators
FLEET’s fruitful relationship with Tsinghua University (Beijing) has been expanded, with the Centre welcoming two new Partner Investigators to lead research collaborations. Prof Shuyun Zhou studies the electronic structure of novel two-dimensional materials and heterostructures using advanced electron spectroscopic tools, including angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), spin-resolved ARPES, nano-ARPES and ultrafast, time-resolved ARPES. She has made important progress on the electronic structure …
Monash engineers unlock avenue for early cancer diagnosis
Monash University engineers have unlocked the door to earlier detection of cancer with a world-first study identifying a potential new testing method that could save millions of lives. Researchers found that a sensor using new, more sensitive materials to look for key markers of disease in the body increased detection by up to 10,000 times. Associate Professor Qiaoliang Bao from …
First snapshot of exciton-polariton condensation process
First snapshot of exciton-polariton Bose-Einstein condensation (BEC) in an inorganic semiconductor Unique opportunity to understand details of BEC without statistical averaging Key to fundamental understanding of exciton-polaritons An ANU advance provides never-before-achieved ‘snapshot’ of Bose-Einstein condensation. Previously, observations of exciton-polaritons in a Bose-Einstein condensate were limited to statistical averaging over millions of condensation events. ‘Snapshot’ imaging of polaritons forming a …
Topological material switched off and on for the first time: key advance for future topological transistors
Significant step toward future topological electronics The first electric field-switchable topological material Topological transistors would be an ultra-low energy , beyond CMOS solution to ICT energy use after the end of Moore’s Law Over the last decade, there has been much excitement about the discovery, recognised by the Nobel Prize in Physics only two years ago, that there are two …
Clarifying effects of negative mass
A FLEET study led by University of Queensland’s David Colas clarifies recent studies of negative mass, investigating the strange phenomenon of self-interference. Negative mass?? When we think of ‘mass’, we usually consider the ‘inertial’ mass – the resistance of a body to acceleration due to an applied force. For a moving object, its mass is then a simple relationship between …
Researchers discover directional, long-lived nanolight in 2D material
An international team led by researchers from Soochow University (Suzhou, China), Monash University (Melbourne, Australia), University of Oviedo (Asturias, Spain), and CIC nanoGUNE (San Sebastián, Spain) have discovered squeezed light (‘nanolight’) in the nanoscale that propagates only in specific directions along thin slabs of molybdenum trioxide – a natural anisotropic 2D material. Besides its unique directional character, this nanolight lives …