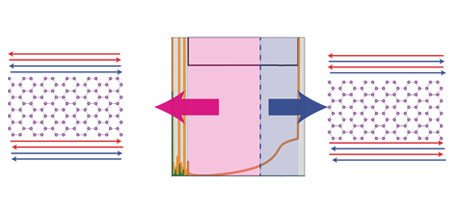
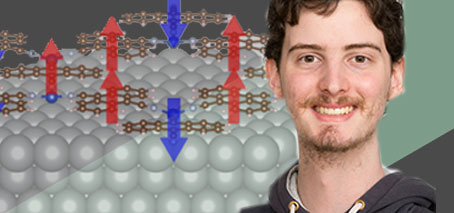
A switchable material based on electron-electron interactions. An Australian-led study has found unusual insulating behaviour in a new atomically-thin material – and the ability to switch it on and off. Materials that feature strong interactions between electrons can display unusual properties such as the ability to act as insulators even when they are expected to conduct electricity. These insulators, known …
Alumni interview: Bernard Field
Bernard Field was one of the earliest of FLEET PhD students, joining the Centre in 2018 originally as an Honours student, then a PhD student in 2019 under Agustin Schiffrin and Nikhil Medhekar. His PhD research focused on correlated electrons in a frustrated 2D lattice, within FLEET’s theme 1. We interviewed Bernard about his career path after leaving FLEET (he …
Infrastructure funding for FLEET researchers
This month’s ARC infrastructure funding round saw FLEET researchers across five universities on teams awarded additional funding towards research facilities, including significant new imaging resources in South Australia and NSW. Pankaj Sharma, initially a FLEET Research Fellow at UNSW and now a Centre AI at Flinders University (South Australia), will help develop new, state-of-the-art atomic force microscopy (AFM) facilities for the …
US-Australia condensed-matter/cold atoms colloquia series
Novel approach to advanced electronics, data storage with ferroelectricity
Published first at Flinders University Latest research from Flinders University and UNSW Sydney, published in the American Chemical Society ACS Nano journal, explores switchable polarization in a new class of silicon compatible metal oxides and paves the way for the development of advanced devices including high-density data storage, ultra low energy electronics, and flexible energy harvesting and wearable devices. The …
‘Topological gardening’ to achieve unexpected spin transport
‘Trimming’ the edge-states of a topological insulator yields a new class of material featuring unconventional ‘two way’ edge transport in a new theoretical study from Monash University, Australia. The new material, a topological crystalline insulator (TCI) forms a promising addition to the family of topological materials and significantly broadens the scope of materials with topologically nontrivial properties. Its distinctive reliance …
Listening to nanoscale earthquakes
A recent UNSW-led paper published in Nature Communications presents an exciting new way to listen to avalanches of atoms in crystals. The nanoscale movement of atoms when materials deform leads to sound emission. This so-called crackling noise is a scale-invariant phenomenon found in various material systems as a response to external stimuli such as force or external fields. Jerky material …
Alex Hamilton, new Industry Laureate Fellow
Unleashing the combined power of electrons and holes for better quantum computing Congratulations to FLEET Deputy Director Prof Alex Hamilton, who has been named an Industry Laureate Fellow by the ARC. Alex and his team at UNSW receive $3.8 million towards ground-breaking silicon-based quantum-computer technology to dramatically speed up computation, enabling Australia to maintain its global lead in quantum technologies. …
Combining irradiation and lithography to engineer advanced conducting materials
A process has been developed to engineer nanoscale arrays of conducting channels for advanced scalable electronic circuitry Using ion implantation and lithography, investigators created patterns of topological surface edge states on a topological material that made the surface edges conductive while the bulk layer beneath remained an insulator Low energy ion implantation, neutron and X-ray reflectometry techniques at ANSTO supported …
Destroying the superconductivity in a kagome metal
Electrically controlled superconductor-to-“failed insulator” transition, and giant anomalous Hall effect in the kagome metal CsV3Sb5 A new RMIT-led international collaboration published in February has uncovered, for the first time, a distinct disorder-driven bosonic superconductor-insulator transition. The discovery outlines a global picture of the giant anomalous Hall effect and reveals its correlation with the unconventional charge density wave in the AV3Sb5 …
Magnetism or no magnetism? The influence of substrates on electronic interactions
How substrates influence magnetism in 2D materials Interaction-induced magnetism in metal-organic frameworks on substrates A new study at Monash University illustrates how substrates affect strong electronic interactions in two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks. Materials with strong electronic interactions can have applications in energy-efficient electronics. When these materials are placed on a substrate, their electronic properties are changed by charge transfer, strain, and …
A new era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics
A UNSW/Flinders University paper published recently in Nature Reviews Materials presents an exciting overview of the emerging field of 2D ferroelectric materials with layered van-der-Waals crystal structures: a novel class of low-dimensional materials that is highly interesting for future nanoelectronics. Future applications include ultra-low energy electronics, high-performance, non-volatile data-storage, high-response optoelectronics, and flexible (energy-harvesting or wearable) electronics. Structurally different from …
New Chief Investigator Priyank Kumar
Congratulations to Priyank Kumar at the School of Chemical Engineering, UNSW Sydney, who becomes a new Chief Investigator within FLEET. “I look forward to contributing to the objectives of FLEET through both fundamental and translational research,” said Priyank. “I would like to thank Michael Fuhrer, Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh and the FLEET team for providing me this opportunity.” Priyank has been an …
Future Fellowship Mark Edmonds
Kagome metals: From Japanese basket to next generation electronic devices FLEET AI Dr Mark Edmonds received an ARC Future Fellowship in this week’s announcement by the Minister. The new ARC Fellowship will support Mark’s work investigating a new type of 2D material that is very promising for faster, more energy-efficient future electronic devices. ‘Kagome’ metals have a topological non-trivial nature …
The hetero-interface is the device: a computational approach
Designing hetero-interfaces towards new optoelectronic functionalities using large-scale computations Assembling ‘Lego-like’ 2D ‘heterostructures’ can give rise to emergent properties and functionalities very different from the intrinsic characteristics of the constituents. Density functional theory (DFT)-based band-structure calculations can shed light on interfacial properties of different heterostructures. Interface properties of 2D perovskite/TMD heterostructures Heterostructures based on different 2D materials have resulted in …
A zigzag blueprint for topological electronics
A collaborative study led by the University of Wollongong confirms switching mechanism for a new, proposed generation of ultra-low energy ‘topological electronics’. Based on novel quantum topological materials, such devices would ‘switch’ a topological insulator from non-conducting (conventional electrical insulator) to a conducting (topological insulator) state, whereby electrical current could flow along its edge states without wasted dissipation of energy. …
Negative capacitance in topological transistors could reduce computing’s unsustainable energy load
Australian researchers have discovered that negative capacitance could lower the energy used in electronics and computing, which represents 8% of global electricity demand. The researchers at four universities within the ARC Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies (FLEET) applied negative capacitance to make topological transistors switch at lower voltage, potentially reducing energy losses by a factor of ten …
Having your cake and eating it too: double-dosing induces magnetism while strengthening electron quantum oscillations in a topological insulator
Harnessing massive Dirac fermions in dual-magnetic-ion-doped Bi2Se3 topological insulator showing extremely strong quantum oscillations in the bulk. Double doping induces a gap for the topological surface state. A University of Wollongong-led team across three FLEET nodes has combined two traditional semiconductor doping methods to achieve new efficiencies in the topological insulator bismuth-selenide (Bi2Se3), Two doping elements were used: samarium (Sm) …
Welcoming Simon Granville (MacDiarmid) new FLEET Partner Investigator
Welcome to FLEET’s long-time collaborator Dr Simon Granville, who this month joins the Centre as a Partner Investigator. Simon is a Principal Investigator at FLEET’s partner organisation the MacDiarmid Institute for Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology, where he leads the Institute’s Future Computing project to control electron transport and spin through superconductivity and topology. As a Senior Scientist at the Robinson …
Electrons on the edge: the story of an intrinsic magnetic topological insulator
An intrinsic magnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4 has been discovered with a large band gap, making it a promising material platform for fabricating ultra-low-energy electronics and observing exotic topological phenomena. Hosting both magnetism and topology, ultra-thin (only several nanometers in thickness) MnBi2Te4 was found to have a large band-gap in a Quantum Anomalous Hall (QAH) insulating state, where the material is …
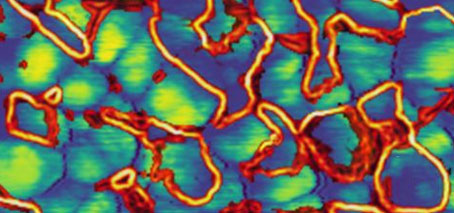
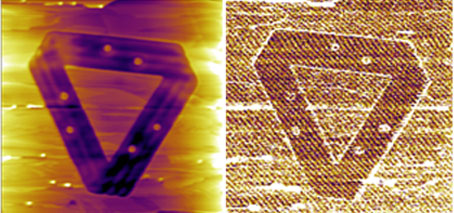
Star attraction: magnetism generated in 2D organic material by star-like arrangement of molecules
2D kagome materials are a platform for tuneable electron-electron interactions ‘Star-like’ atomic-scale kagome geometry ‘switches on’ magnetism in a 2D organic material A 2D nanomaterial consisting of organic molecules linked to metal atoms in a specific atomic-scale geometry shows non-trivial electronic and magnetic properties due to strong interactions between its electrons. A new study, published today, shows the emergence of …
Home-grown semiconductors for faster, smaller electronics
‘Growing’ electronic components directly onto a semiconductor block avoids messy, noisy oxidation scattering that slows and impedes electronic operation. A UNSW study out this month shows that the resulting high-mobility components are ideal candidates for high-frequency, ultra-small electronic devices, quantum dots, and for qubit applications in quantum computing. Smaller means faster, but also noisier Making computers faster requires ever-smaller transistors, …
¡Felicidades! Fellowship success for Dr Iolanda Di Bernardo
Congratulations to FLEET Research Fellow Dr Iolanda Di Bernardo (Monash), who has received the highly prized Juan de la Cierva fellowship to fund research in Spain, starting in Spring 2022. The Juan de la Cierva fellowship is highly competitive, with a success rate between 10 and 15%, and is similar to the Australian DECRA fellowship. The grants encourage the recruitment …
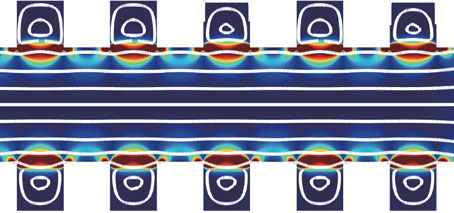
A Smooth Conduit for Electron Fluids
—first published APS Physics Electrons flow like a viscous fluid through a 2D channel with perfectly smooth sidewalls, offering a new platform to test solid-state and fluid dynamics theories. Electrons can, under certain conditions, flow like a fluid that’s thicker than honey. Now researchers have managed to observe this viscous fluid behavior in a way that allows unambiguous measurements and …
Mixing a cocktail of topology and magnetism for future electronics
Monash review: joining topological insulators with magnetic materials for energy-efficient electronics A new Monash review throws the spotlight on recent research in heterostructures of topological insulators and magnetic materials. In such heterostructures, the interesting interplay of magnetism and topology can give rise to new phenomena such as quantum anomalous Hall insulators, axion insulators and skyrmions. All of these are promising …
Video explainers for 3MT
Tackling the next climate crisis with polariton superfluids, chocolate bars, ultra-fast laser pulses and chaotic gardening… FLEET’s Rishabh Mishra (Swinburne), Mitko Oldfield and Alex Nguyen (both at Monash University) have recently recorded explanations of their PhD research, submitted for the 2021 national Three Minute Thesis competition. Mitko Oldfield (School of Physics and Astronomy) explains his studies of polariton superfluids, with …
Identifying a topological fingerprint
Generating a topological anomalous Hall effect in a non-magnetic conductor anomalous planar Hall effect (APHE) the ‘smoking gun’ for the topological magnetic monopole in momentum space A FLEET theoretical study out this week has found a ‘smoking gun’ in the long search for the topological magnetic monopole referred to as the Berry curvature. This discovery is a breakthrough in the …
Congratulations Meera Parish and Agustin Schiffrin
Congratulations to two of FLEET’s Chief Investigators, whose contributions have recently been recognised by the School of Physics and Astronomy at Monash University: Meera Parish promoted to full Professor Agustin Schiffrin promoted to Associate Professor Prof Meera Parish (right) is a theoretical physicist developing many-body theories that span electron-hole systems and ultracold atomic gases. She is an ARC Future Fellow …
Women in FLEET Honours students at RMIT, UNSW, ANU
Please welcome FLEET’s three new Women in FLEET Honours students: Kyla Rutherford (RMIT) Olivia Kong (UNSW) Robin Hu (ANU) Kyla, Olivia and Robin have all received Women in FLEET Honours Scholarships, which are awarded to high performing students doing their Honours research project with FLEET. Kyla Rutherford will be working with Jared Cole at RMIT to understand transport properties in …
Electrons on the edge: Atomically-thin quantum spin Hall materials
An exotic class of topological quantum materials has been reviewed by an international team of physicists, led by A/Prof Bent Weber at Nanyang Technological University (NTU – Singapore). Atomically-thin quantum spin Hall insulators, whose electronic states are protected by topology, promise applications in quantum information processing. Quantum spin Hall insulators are a class of two-dimensional (2D) topological states of matter …