Monash review: joining topological insulators with magnetic materials for energy-efficient electronics A new Monash review throws the spotlight on recent research in heterostructures of topological insulators and magnetic materials. In such heterostructures, the interesting interplay of magnetism and topology can give rise to new phenomena such as quantum anomalous Hall insulators, axion insulators and skyrmions. All of these are promising …
New 2D research hub features FLEET talent
A new ARC Research Hub highlighting the role of novel and 2D materials in emerging technologies in fields such as energy storage, purification and printed electronics features FLEET talent amongst its team. The ARC Research Hub for Advanced Manufacturing with 2D Materials (AM2D) will be led by Prof Mainak Majumder (Monash Department of Mechanical Engineering). Two FLEET Chief Investigators are amongst …
Video explainers for 3MT
Tackling the next climate crisis with polariton superfluids, chocolate bars, ultra-fast laser pulses and chaotic gardening… FLEET’s Rishabh Mishra (Swinburne), Mitko Oldfield and Alex Nguyen (both at Monash University) have recently recorded explanations of their PhD research, submitted for the 2021 national Three Minute Thesis competition. Mitko Oldfield (School of Physics and Astronomy) explains his studies of polariton superfluids, with …
Reviewing pressure effects on iron-based high-temperature superconductors
Fe-based superconductors reviewed The discovery of iron-based superconductors with a relatively high transition temperature Tc in 2008 opened a new chapter in the development of high-temperature superconductivity. The following decade saw a ‘research boom’ in superconductivity, with remarkable achievements in the theory, experiments and applications of iron-based superconductors, and in our understanding of the fundamental mechanism of superconductivity. A UOW …
Inducing and tuning spin interactions in layered material by inserting iron atoms, protons
Controlling Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (DMI) in chiral magnet iron-doped tantalum-sulfide by proton intercalation Magnetic-spin interactions that allow spin-manipulation by electrical control allow potential applications in energy-efficient spintronic devices. An antisymmetric exchange known as Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interactions (DMI) is vital to form various chiral spin textures, such as skyrmions, and permits their potential application in energy-efficient spintronic devices. Published this week, a Chinese-Australia …
Women in FLEET Honours students at RMIT, UNSW, ANU
Please welcome FLEET’s three new Women in FLEET Honours students: Kyla Rutherford (RMIT) Olivia Kong (UNSW) Robin Hu (ANU) Kyla, Olivia and Robin have all received Women in FLEET Honours Scholarships, which are awarded to high performing students doing their Honours research project with FLEET. Kyla Rutherford will be working with Jared Cole at RMIT to understand transport properties in …
Tools of the Trade: Iolanda Di Bernardo explains XPS depth profiling for Nature series
X- ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is used for material characterization, providing quantitative information on the chemical composition of materials by identifying the type of elements that are present (nowadays, with a detection limit in the range of one part per thousand). XPS also allows the identification of the chemical state of the elements – such as the types of bonds …
Liquid metals spin-off launched
The Liquid-metals spin-off company Liquid Metal Plus (LM+) initiated in 2020 with FLEET investigators Kourosh Kalantar-Zadeh (UNSW) and Dr Torben Daeneke (RMIT), together with Dorna Esrafilzadeh (UNSW), was launched in April 2021. Pushing print on flexible touchscreens Climate rewind: turning CO2 back into coal The company has two areas of focus, with the unifying theme being application of liquid-metal technologies …
Explainer: Linkage funding for topological-thermoelectricity
A team led by FLEET CI Prof Xiaolin Wang (University of Wollongong) has won a linkage project for topological materials based thermoelectricity. Thermoelectricity can directly convert heat to electrical energy or vice-versa. It plays an important role in renewable and sustainable energy by harvesting waste heat, which is widely available in human body, computer chips, sunlight and steel industry. Thermoelectric …
Thermoelectric devices convert waste heat from industry into viable new energy source
New research supports development of thermoelectric devices to convert waste heat from industry into a viable new energy source Australian industries could benefit from being able to harness the heat by-products from operations Development of advanced materials can sustainably convert waste heat into useful forms of energy to benefit Australia. The work will be undertaken as part of an Australian …
Tools of the Trade: Zengji Yue explains ion intercalation for new Nature series
Inserting ions into, or between, atomically-thin materials can be used to alter their properties in a finely-controlled fashion. For example, graphene’s properties can be fine-tuned by injection of another material (a process known as ‘intercalation’) either underneath the graphene, or between two graphene sheets. (See article.) “Intercalating ions into layered materials increases the spacing and decreases the coupling between the …
A new, positive approach could be the key to next-generation, transparent electronics
A new study, out this week, could pave the way to revolutionary, transparent electronics. Such see-through devices could potentially be integrated in glass, in flexible displays and in smart contact lenses, bringing to life futuristic devices that seem like the product of science fiction. For several decades, researchers have sought a new class of electronics based on semiconducting oxides, whose …
‘Target identified’: teaching a machine how to identify imperfections in 2D materials
Applying machine learning to automated characterisation of atomically-thin materials Just as James Cameron’s Terminator-800 was able to discriminate between “clothes, boots, and a motorcycle”, machine-learning could identify different areas of interest on 2D materials. The simple, automated optical identification of fundamentally different physical areas on these materials (eg, areas displaying doping, strain, and electronic disorder) could significantly accelerate the science …
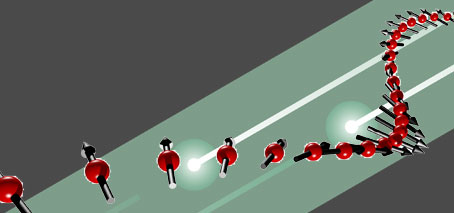
Harnessing socially-distant molecular interactions for future computing
Could long-distance interactions between individual molecules forge a new way to compute? Interactions between individual molecules on a metal surface extend for surprisingly large distances – up to several nanometers. A new study, just published, of the changing shape of electronic states induced by these interactions, has potential future application in the use of molecules as individually addressable units. For …
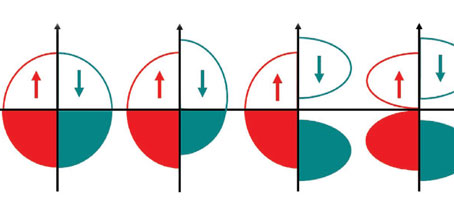
Electrical spin filtering the key to ultra-fast, energy-efficient spintronics
Spin-filtering could be the key to faster, more energy-efficient switching in future spintronic technology, allowing the detection of spin by electrical rather than magnetic means. A paper published last month by researchers at UNSW and international collaborators demonstrates spin detection using a spin filter to separate spin orientation according to their energies. Ultra-fast, ultra-low energy ‘spintronic’ devices are an exciting, …
Game-changer in thermoelectric materials: decoupling electronic and thermal transport
new thermoelectric materials could unlock body-heat powered personal devices, such as wrist-watches A new University of Wollongong study overcomes a major challenge of thermoelectric materials, which can convert heat into electricity and vice versa, improving conversion efficiency by more than 60%. Current and potential future applications range from low-maintenance, solid-state refrigeration to compact, zero-carbon power generation, which could include small, …
Reviewing multiferroics for future, low-energy data storage
Multiferroic BFO’s unique magnetic and electrical properties offer possible ultra-low energy data storage A new UNSW study comprehensively reviews the magnetic structure of the multiferroic material bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3 – BFO). The review advances FLEET’s search for low-energy electronics, bringing together current knowledge on the magnetic order in BFO films, and giving researchers a solid platform to further develop this …
Liquid metals come to the rescue of semiconductors
Moore’s law is an empirical suggestion describing that the number of transistors doubles every few years in integrated circuits (ICs). However, Moore’s law has started to fail as transistors are now so small that the current silicon-based technologies are unable to offer further opportunities for shrinking. One possibility of overcoming Moore’s law is to resort to two-dimensional semiconductors. These two-dimensional materials …
Next-generation multi-state data storage: leaving binary behind
International collaboration reviews future data-storage technology that steps ‘beyond binary’, storing more data than just 0s and 1s Electronic data is being produced at a breath-taking rate. The total amount of data stored in data centres around the globe is of the order of ten zettabytes (a zettabyte is a trillion gigabytes), and we estimate that amount doubles every couple …
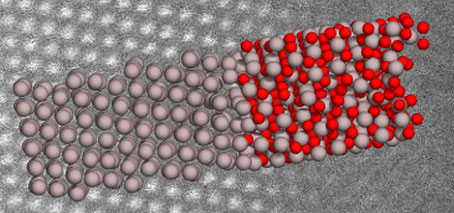
What happens between the sheets? ‘Floating’ graphene on a bed of calcium atoms
Adding calcium to graphene creates an extremely-promising superconductor, but where does the calcium go? Adding calcium to a composite graphene-substrate structure creates a high transition-temperature (Tc) superconductor. In a new study, an Australian-led team has for the first time confirmed what actually happens to those calcium atoms: surprising everyone, the calcium goes underneath both the upper graphene sheet and a …
Reviewing the Quantum Anomalous Hall Effect (QAHE)
Quantum anomalous Hall effect (QAHE)-materials reviewed Magnetic topological insulators and spin-gapless semiconductors A collaboration across three FLEET nodes has reviewed the fundamental theories underpinning the quantum anomalous Hall effect (QAHE). QAHE is one of the most fascinating and important recent discoveries in condensed-matter physics. It is key to the function of emerging ‘quantum’ materials, which offer potential for ultra-low energy …
Unexpectedly-fast conduction electrons in Na3Bi
—Written by Dr Iolanda di Bernardo, FLEET/Monash An Australian-led study uses a scanning-tunnelling microscope ‘trick’ to map electronic structure in Na3Bi, seeking an answer to that material’s extremely high electron mobility. In studying the topological Dirac semimetal, the team found that exchange and correlation effects are crucial to electron speed, and therefore mobility, and thus to the use of this …
Through the nanoscale looking glass: FLEET researchers determine boson peak frequency in ultra-thin alumina
There’s more to glass than meets the eye. Glasses, which are disordered materials with no long-range chemical order, have some mysterious properties that have remained enigmatic for several decades. Amongst these are the anomalous vibrational states that contribute to the heat capacity at low temperature. Early researchers established that these states obey Bose-Einstein statistics, and the name stuck, so today …
Liquid metal synthesis for better piezoelectrics: atomically-thin tin-monosulfide
Record output power obtained from piezoelectric, atomically-thin material Remarkable synthesis advance for materials such as tin-monosulfide (group IV monochalcogenides), which are predicted to exhibit strong piezoelectricity Potential materials for future wearable electronics and other motion-powered, energy-harvesting devices RMIT-UNSW collaboration applies liquid-metal synthesis to piezoelectrics, advancing future flexible, wearable electronics, and biosensors drawing their power from the body’s movements. Materials such …
Spin-gapless semiconductors review: more candidates for next-generation low energy and high efficient spintronics
Spin-gapless semiconductors (SGSs) are a new class of zero-gap materials, with fully spin polarized electrons and holes. SGSs bridge the zero-gap materials and half-metals Material’s fascinating spin and charge states hold great potential for future spintronic technology. A University of Wollongong team has published an extensive review of spin-gapless semiconductors (SGSs) . Spin gapless semiconductors (SGSs) are a new class …
Applying ‘magic angle’ twistronics to manipulate the flow of light
‘Twisted’ layers of 2D materials produce photonic topological transition at ‘magic’ rotation angles Principles of Moire-pattern bilayer graphene applied to 2D material photonics for first time Monash researchers are part of an international collaboration applying ‘twistronics’ concepts (the science of layering and twisting 2D materials to control their electrical properties) to manipulate the flow of light in extreme ways. The …
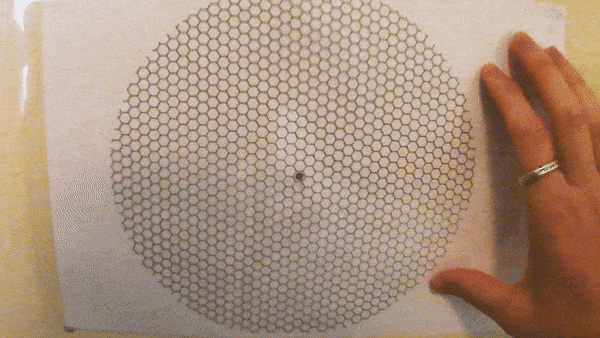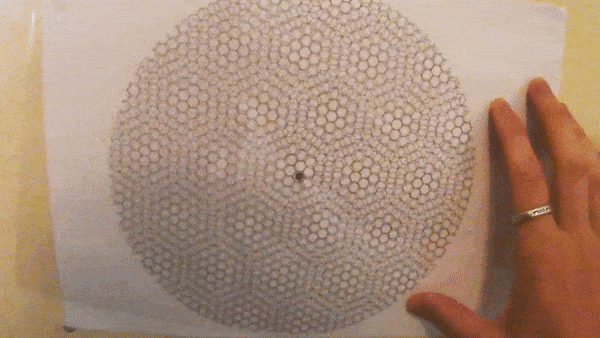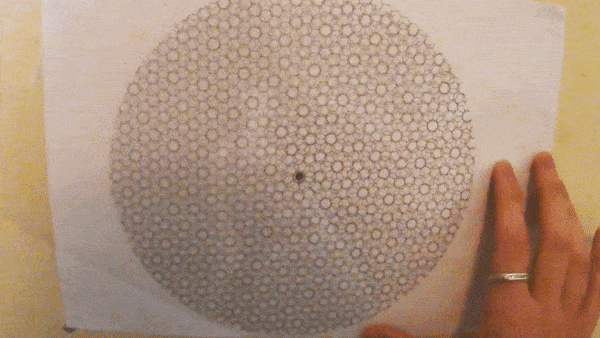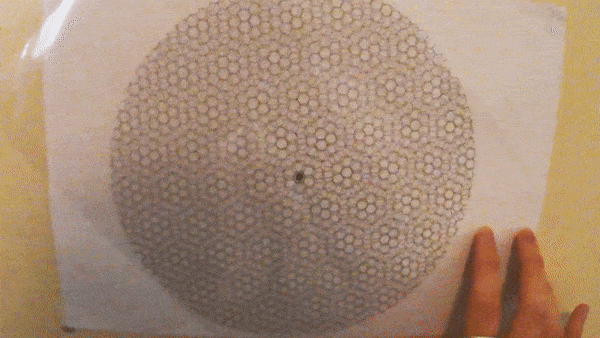
Explainer: Moire patterns in graphene and plastic
A recent FLEET homescience exercise explained how simple geometric patterns printed on transparency (‘overhead projector sheets’, to those of us old enough to remember such technology), and overlaid at varying angles, produced a combined ‘Moire’ pattern of varying dimensions. Two sheets of repeating squares produces a Moire pattern of larger squares. Two sheets of repeating triangles produces a Moire pattern …
Interfaces the key in atomically-thin, ‘high temperature’ superconductors
An international FLEET collaboration publishing a review of atomically-thin ‘high temperature’ superconductors finds that each has a common driving mechanism: interfaces. The team, including researchers from the University of Wollongong, Monash University and Tsinghua University (Beijing), found that interfaces between materials were the key to superconductivity in all systems examined. The enhancement of superconductivity at interfaces (interface superconductivity enhancement effect) …
Kirrily Rule live-streamed neutron-scattering talk to the AIP
FLEET Partner Investigator Kirrily Rule (ANSTO) introduced an audience of over 100 to the use of neutron scattering in material analysis last week, in a live-streamed seminar co-hosted with the Australian Institute of Physics. Neutron scattering is a powerful tool for investigating the structure and dynamics of condensed matter systems. In particular the magnetic spin of the neutron can interact …
Studying phonon-polaritons in hBN
Phonon-polaritons in layered crystals have peculiar properties where they occur at the boundary between materials. In a new study led from UNSW, phonon-polaritons were studied in thin-layer hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) by combined scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Prof Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh’s multidisciplinary group at UNSW combined scattering-SNOM single-wavelength imaging and broadband scattering IR …