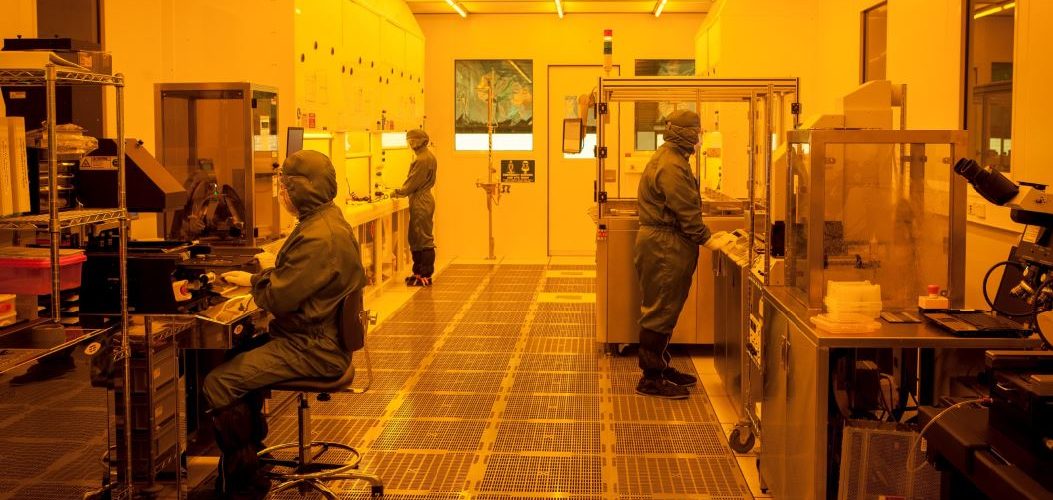
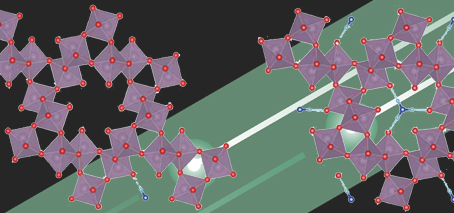
International collaboration reviews future data-storage technology that steps ‘beyond binary’, storing more data than just 0s and 1s Electronic data is being produced at a breath-taking rate. The total amount of data stored in data centres around the globe is of the order of ten zettabytes (a zettabyte is a trillion gigabytes), and we estimate that amount doubles every couple …
Using protons to tune interlayer forces in van-der-Waals materials
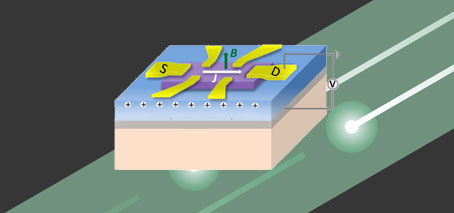
Interlayer coupling in vdW material Fe3GeTe2 successfully increased by insertion of protons A Chinese-Australian collaboration has demonstrated for the first time that interlayer coupling in a van der Waals (vdW) material can be largely modulated by a protonic gate, which inject protons to devices from an ionic solid. The discovery opens the way to exciting new uses of vdW materials, …
Liquid metal synthesis for better piezoelectrics: atomically-thin tin-monosulfide
Record output power obtained from piezoelectric, atomically-thin material Remarkable synthesis advance for materials such as tin-monosulfide (group IV monochalcogenides), which are predicted to exhibit strong piezoelectricity Potential materials for future wearable electronics and other motion-powered, energy-harvesting devices RMIT-UNSW collaboration applies liquid-metal synthesis to piezoelectrics, advancing future flexible, wearable electronics, and biosensors drawing their power from the body’s movements. Materials such …
FLEETs Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh awarded prestigious prize
FLEET CI Professor Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh (UNSW Sydney) has been awarded the prestigious 2020 Robert Boyle Prize for Analytical Science by The Royal Society of Chemistry. Prof Kalantar-zadeh is recognised for his significant influence across multiple fields of engineering. Contributions to society coming from his research across multiple disciplines include new innovative pollution sensors, transistors, medical devices and optical systems. Many …
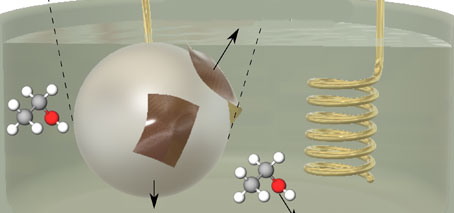
Liquid metals break down organic fuels into ultra-thin graphitic sheets
For the first time, FLEET researchers at UNSW, Sydney show the synthesis of ultra-thin graphitic materials at room temperature using organic fuels (which can be as simple as basic alcohols such as ethanol). Graphitic materials, such as graphene, are ultra-thin sheets of carbon compounds that are sought after materials with great promises for battery storage, solar cells, touch panels and …
Studying phonon-polaritons in hBN
Phonon-polaritons in layered crystals have peculiar properties where they occur at the boundary between materials. In a new study led from UNSW, phonon-polaritons were studied in thin-layer hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) by combined scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Prof Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh’s multidisciplinary group at UNSW combined scattering-SNOM single-wavelength imaging and broadband scattering IR …
Nano-thin flexible touchscreens could be printed like newspaper
Researchers have developed an ultra-thin and ultra-flexible electronic material, able to be printed and rolled out like newspaper, for the touchscreens of the future. The touch-responsive technology is 100 times thinner than existing touchscreen materials and so pliable it can be rolled up like a tube. To create the new conductive sheet, an RMIT University-led team used a thin film …
Collaboration unlocks new magnetic properties for future, faster, low-energy spintronics
• RMIT–UNSW collaboration combines theory, experimental expertise • ‘Spintronic’ applications promise faster, more efficient computing • New magnetic properties of 2D Fe3GeTe2 (FGT) discovered A theoretical–experimental collaboration across two FLEET nodes has discovered new magnetic properties within 2D structures, with exciting potential for researchers in the emerging field of ‘spintronics’. Spintronic devices use a quantum property known as ‘spin’, in …
Meet molybdenum, an acid-free route to future Hydrogen power?
Molybdenum based compounds could provide key to hydrogen production for future zero-emissions energy RMIT/Monash collaboration opens promising route towards alkaline hydrogen production A FLEET study combining experimental expertise at RMIT with theoretical modelling at Monash University opens a new route towards efficient, cost-effective production of hydrogen. Researchers discovered that ammonium-doped, hexagonal molybdenum oxide (MoO3) displays extremely promising electronic and material …
Using disorder to build new materials for low-energy electronics: welcome new FLEET AI Julie Karel
Dr Julie Karel conducts research at the intersection of materials science and condensed matter physics to develop new materials for emerging low-energy nanoelectronic and magnetoelectronic devices. Originally from the US, Julie developed new thermal interface materials to improve mobile-device performance at Intel, and was a postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute in Germany. In materials design, Julie uses complete …
Researchers discover directional, long-lived nanolight in 2D material
An international team led by researchers from Soochow University (Suzhou, China), Monash University (Melbourne, Australia), University of Oviedo (Asturias, Spain), and CIC nanoGUNE (San Sebastián, Spain) have discovered squeezed light (‘nanolight’) in the nanoscale that propagates only in specific directions along thin slabs of molybdenum trioxide – a natural anisotropic 2D material. Besides its unique directional character, this nanolight lives …
Pushing ‘print’ on large-scale piezoelectric materials
First ever large-scale 2D surface deposition of piezoelectric material Simple, inexpensive technique opens new fields for piezo-sensors & energy harvesting Researchers have developed a revolutionary method to ‘print’ large-scale sheets of two dimensional piezoelectric material, opening new opportunities for piezo-sensors and energy harvesting. Importantly, the inexpensive process allows the integration of piezoelectric components directly onto silicon chips. Until now, no …
Centre collaboration combines material expertise
FLEET RMIT—UNSW collaboration measuring transport properties of van der Waals heterostructures FLEET PhD Cheng Tan (RMIT) visited UNSW’s labs in May to perform magnetic coupling measurements on 2D ferromagnetic crystals. The visit was reciprocated this month with FLEET Research Fellow Feixiang Xiang (UNSW) visiting RMIT to construct van der Waals structures for studying of 2D topological systems. This collaboration between …
Thinner is better: van der Waals (vdW) material shows the right stuff at 200 nanometres
The unusual electronic and magnetic properties of van der Waals (vdW) materials, made up of many ‘stacked’ 2D layers, offer potential for future electronics, including spintronics. In a recent study, FLEET researchers at RMIT found that one promising candidate material, Fe3GeTe2 (FGT), fits the bill – provided it’s created in layers only 200 millionths of a millimetre in thickness. This …
FLEET’s Qiaoliang Bao a champion of Australian nanotech
FLEET-nano collaboration recognised: Congratulations to Qiaoliang Bao, 2018 ANFF-VIC Technology Fellow Qiaoliang Bao works at the nanoscale, trapping photons in atomically-thin, two-dimensional materials, where high binding energies create a quantum state known as a superfluid. The aim is a new generation of superfluid transistors that will ‘switch’ using much less energy than conventional electronics. Such work requires access to the …
Custom, nanoscale structures on demand at RMIT
“Endless” possibilities for custom nanotech design FLEET’s research to achieve zero-dissipation electrical current depends on the design of key nanoscale structures. Within FLEET, nano-device fabrication is coordinated via Enabling technology B, which links each of the research themes. In 2017, Theme B leader Lan Wang, and PhD student Cheng Tan, developed a method to build such nanoscale structures, required to achieve zero-dissipation …
Ingestible smart pill recognised
Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh’s ingestible smart pill could revolutionise prevention and diagnosis of gut disorders/disease, and make a significant difference to the health of as many as one in five Australians who suffer gut disorders. This month the technology won the prestigious 2017 IEEE Sensors Council achievement award in the field of sensors. Read more at RMIT. At RMIT,Prof Kalantar-zadeh is Director …
Materials one atom thick & nanotransistors: FLEET features in nano edition
FLEET features in this month’s annual ‘nano’ edition of the Australian Manufacturing Tech magazine. The article looks at growth of atomically thin and other novel materials and nanofabrication, with a particular focus on partnerships. Atomically thin material projects presented include semiconductor fabrication at RMIT University (Lan Wang) and the University of Wollongong (Xiaoliang Wang) and molecular beam epitaxy (Mark Edmonds …
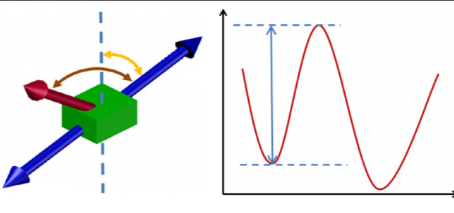
Band alignment at semiconductor junction looking good for low-resistance contacts
The future of ultra-low resistance semiconductor junctions in novel low-energy electronics is looking good after a recent study took a very close look at band alignment. FLEET is using two-dimensional materials in the search for new electronics devices that will carry electrical current without losing the significant energy dissipated in current, silicon technology. The new electronic devices developed at FLEET …
- Page 2 of 2
- 1
- 2