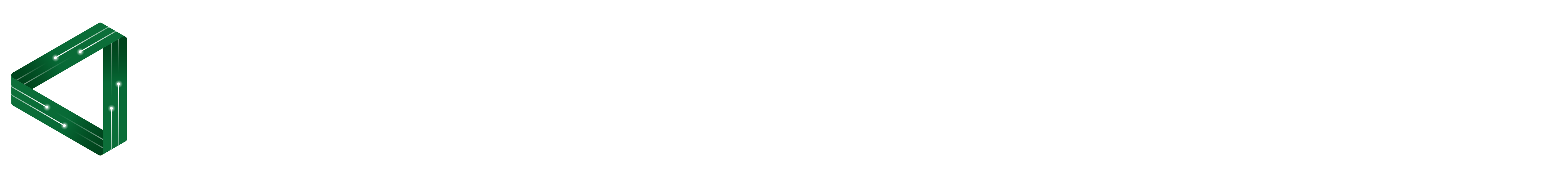
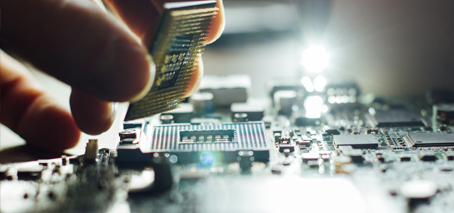
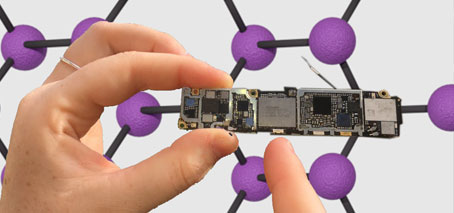
X- ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is used for material characterization, providing quantitative information on the chemical composition of materials by identifying the type of elements that are present (nowadays, with a detection limit in the range of one part per thousand). XPS also allows the identification of the chemical state of the elements – such as the types of bonds …
Engaging public conversations at Melbourne Knowledge Week
Melbourne Knowledge Week (26 April-2 May 2021) was an opportunity for FLEET to engage with over 350 members of the public about the exciting future of computing, and the vital role of energy-efficient electronics in that future. FLEET’s sustainable computing booth ran for the full week at the festival hub, with hands-on science demonstrations linked to materials used in FLEET …
FLEET reps at Science meets Parliament
FLEET had four researchers at STA’s annual Science Meets Parliament, which was fully online in 2021, other than regional gala dinners. Participants heard from a diverse mix of Australia’s top scientists, including Chief Scientist Cathy Foley and Chief Defence Scientist Tanya Monro. FLEET’s four ECR delegates—Eli Estrecho (ANU), Peggy (Qi) Zhang (UNSW), Gary Beane (Monash) and Harley Scammell (UNSW)—were introduced …
Maintaining international links in the absence of international travel
US–Australian transpacific condensed-matter talks The temporary halt in international visits that traditionally spark and fuel research collaborations in 2020 pushed FLEET to find new ways to connect. Some positives have surfaced amid the negative impacts of Covid-19 travel bans on science collaboration, including the expansion in videoconferencing allowing researchers from geographically isolated regions to connect. Together with Centre partners at …
Engaging with industry in 2020
FLEET is building links with partners interested in novel electronic devices and systems working towards the overarching goal of creating pathways to translations of research outcomes. Progress towards this important goal in 2020 included: Adding topological transistors to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) International Roadmap for Devices and Systems Lodging two provisional patents: topological switching (Fuhrer Monash and …
Topological-switching patents demonstrate FLEET’s dominance in field
Two patent applications, one filed in 2020, reinforce FLEET’s position as a world leader in topological transistors. The patents cover work in the ‘switching’ of topological material, to facilitate creation of a functioning topological transistor – a proposed new generation of ultra-low energy electronic devices. Their world-first success was the switching of a material via application of an electric-field between …
Topological materials beat Boltzmann’s tyranny: Surpassing lower limit on computing energy consumption
Topological insulators can reduce transistor switching energy by a factor of four Defeating Boltzman’s tyranny, which puts a lower limit on operating voltage New FLEET research confirms the potential for topological materials to substantially reduce the energy consumed by computing. The collaboration of FLEET researchers from University of Wollongong, Monash University and UNSW have shown in a theoretical study that …
FLEET PhDs on the Melbourne airways
Three FLEET PhD students this month featured on popular radio science show Einstein a go-go, on the show’s regular “20 PhDs in 20 minutes” segment. In this format, student and host each get a minute, covering the student’s entire project in just two minutes combined. (Perfect practice for the famous ‘elevator pitch’.) The three FLEET presenters were Alex Nguyen (Monash), Matt …
Engaging senior school students at JMSS in 2020
In 2020, FLEET continued the Year 10 ‘Future electronics’ course launched the year before in partnership with John Monash Science School (JMSS), Victoria. As well as covering the history of semiconductors, Moore’s Law and computing, the course introduces quantum physics at an intuitive level (with minimal maths) and expands on this fundamental understanding to explain complex, useful quantum states such …
‘Target identified’: teaching a machine how to identify imperfections in 2D materials
Applying machine learning to automated characterisation of atomically-thin materials Just as James Cameron’s Terminator-800 was able to discriminate between “clothes, boots, and a motorcycle”, machine-learning could identify different areas of interest on 2D materials. The simple, automated optical identification of fundamentally different physical areas on these materials (eg, areas displaying doping, strain, and electronic disorder) could significantly accelerate the science …
Harnessing socially-distant molecular interactions for future computing
Could long-distance interactions between individual molecules forge a new way to compute? Interactions between individual molecules on a metal surface extend for surprisingly large distances – up to several nanometers. A new study, just published, of the changing shape of electronic states induced by these interactions, has potential future application in the use of molecules as individually addressable units. For …
‘Pivoting’ to virtual: online lab tours in 2020
In the absence of in-house lab tours to introduce school students to working labs and researchers, in 2020 FLEET developed and distributed a series of ‘virtual lab tours’, of varying levels of interactivity: Show-and-tell lab tour via webcam for John Monash Science School (JMSS) students at Clayton of FLEET laboratories at UNSW in Sydney (materials science), and Swinburne University in …
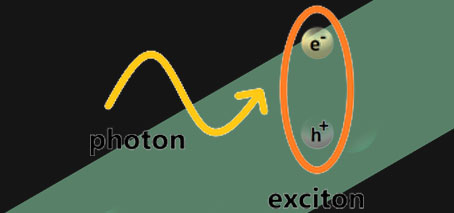
Polariton interactions: Light matters
Enhanced interactions through strong light-matter coupling Why do two-dimensional exciton-polaritons interact? The intriguing quasiparticle the exciton-polariton is part light (photon), and part matter (exciton). Their excitonic (matter) part confers them the ability to interact with other particles —a property lacking to bare photons. In theory, when confined to only two dimensions, very slow (ie, very cold) excitons should cease any …
Supporting future science leaders
FLEET is committed to developing Australia’s next generation of science leaders, and to improving on the current imbalance of women in higher positions in STEM. Career support for women in FLEET works towards each of these two goals, providing an environment in which early-career women can thrive and progress, growing into capable and confident leaders. Four FLEET women were successful …
ARC funding for FLEET investigators
Australia’s Minister for Education Dan Tehan announced $280 million in funding for new research collaborations to start next year. This month’s ARC Discovery Project and Linkage Project funding announcement includes eight grants for projects and facilities led by or involving FLEET researchers. While these projects are distinct from FLEET’s mission to build low-energy electronics, they testify to the capacity FLEET …
Remote science-outreach ‘wow’s students
Distance and Covid will not stop science-outreach. Thank you Zoom!** **not a paid partnership : ) Students at Elsternwick Primary School in Victoria had the opportunity to learn about electrical power, in a hands-on exercise guided by on-screen FLEET members, and following two of the experiments from FLEET’s comprehensive Home Science library. “A unanimous ‘WOW!’ came from all four classrooms …
Temperature evolution of impurities in a quantum gas
What role does heat play in quantum impurity studies? A new, Monash-led theoretical study advances our understanding of its role in thermodynamics in the quantum impurity problem. Quantum impurity theory studies the behaviour of deliberately introduced atoms (ie, ‘impurities’) that behave as particularly ‘clean’ quasiparticles within a background atomic gas, allowing a controllable ‘perfect test bed’ study of quantum correlations. …
Leading Edge: Women Leading Australia
–by Iolanda Di Bernardo and Hareem Khan WLA’s Leading Edge program is designed to help women in their first leading position to develop their leadership skills, enabling the transition of aspiring and early-career female managers into confident, capable and motivated leaders. Throughout the six-month course participants are presented with topics including elements of a successful team / personal styles interpersonal …
FLEET physics a finalist in 2020 Eureka prizes
FLEET physicists from Monash University and the University of Queensland are finalists, named today, in the Australian Museum Eureka Prizes – the nation’s top science awards. The Australian Quantum Vortex team provided the first proof of a 70-year-old theory of turbulence. Turbulence is everywhere, but remains one of physics’ great unsolved problems. Turbulence in two-dimensional flow, and the giant vortices …
To kill a quasiparticle: a quantum whodunit
What causes quasiparticle death? In large systems of interacting particles in quantum mechanics, an intriguing phenomenon often emerges: groups of particles begin to behave like single particles. Physicists refer to such groups of particles as quasiparticles. Understanding the properties of quasiparticles may be key to comprehending, and eventually controlling, technologically important quantum effects like superconductivity and superfluidity. Unfortunately, quasiparticles are …
What happens between the sheets? ‘Floating’ graphene on a bed of calcium atoms
Adding calcium to graphene creates an extremely-promising superconductor, but where does the calcium go? Adding calcium to a composite graphene-substrate structure creates a high transition-temperature (Tc) superconductor. In a new study, an Australian-led team has for the first time confirmed what actually happens to those calcium atoms: surprising everyone, the calcium goes underneath both the upper graphene sheet and a …
Julie Karel describing search for future memory, for Materials Australia
An online audience of almost 90 tuned in this week to hear FLEET CI Dr Julie Karel describing her search for non-volatile memory technologies and associated materials challenges. The talk was co-hosted by FLEET and Materials Australia. Catch up on the talk here Julie described her own work at Monash Department of Material Science and Engineering developing materials that can …
Unexpectedly-fast conduction electrons in Na3Bi
—Written by Dr Iolanda di Bernardo, FLEET/Monash An Australian-led study uses a scanning-tunnelling microscope ‘trick’ to map electronic structure in Na3Bi, seeking an answer to that material’s extremely high electron mobility. In studying the topological Dirac semimetal, the team found that exchange and correlation effects are crucial to electron speed, and therefore mobility, and thus to the use of this …
Bingeing Netflix under lockdown? Here’s why streaming comes at a cost to the environment
Coronavirus lockdowns have led to a massive reduction in global emissions, but there’s one area where energy usage is up – way up – during the pandemic: internet traffic. Data-intensive video streaming, gaming and livestreaming for business, university and school classes, is chewing up energy. Read more: Netflix has capitalized on social isolation, but will its success continue in a post-coronavirus world? Estimates can be notoriously difficult and depend on the electricity …
Congratulations Meera Parish: ARC Future Fellowship
Congratulations to FLEET CI A/Prof Meera Parish who received an ARC Future Fellowship in this week’s announcement. “The revolution in electronics and the Information Age were enabled by powerful theories based on the concept of the quasiparticle, an object composed of many particles such as electrons,” writes A/Prof Parish. The new ARC Fellowship will support Meera’s work to unravel the …
Matt Gebert: outreach champion
Congratulations to FLEET PhD student Matt Gebert, recognised for his dedication to science-outreach by the Monash Faculty of Science. Matt’s contributions to science outreach include running lab tours with Monash Tech School, demonstrating levitating superconductors and speaking at Monash University open day, teaching regional students via the Emerging Science Victoria program, coordinating PhD day, and in-class demos and talks, including …
Behind the scenes at Monash
Shooting for an all-online open day featuring FLEET’s material labs at Monash University’s New Horizons building, FLEET Research Fellow Dr Semonti Bhattacharyya with School of Physics and Astronomy Steve Morton. See the resulting video on Monash Physics youtube.
International collaboration unlocks vdW heterostructure
2D vdW TMD heterostructures studied Study correlates interface physics to device performance An India-Australian theoretical and experimental study for high-performance optoelectronics has been published in Nano Letters. The Monash University collaboration with the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IITB) designed and fabricated a heterostructure comprising two layered transition metal dichalcogenides (WSe2 and ReS2). Integrating new physics in vdW heterostructures Van-der-Waals …
ANSTO Scholarship for FLEET PhD Qile Li
Congratulations to FLEET PhD student Qile Li, whose excellent work in probing electronic structures of novel materials has been recognised by an award and scholarship from the Australian Institute of Nuclear Science and Engineering (AINSE). At ANSTO’s Australian Synchrotron, Qile Li uses Angle-Resolved Photo-Electron Spectroscopy (ARPES) to measure electronic properties of intrinsic magnetic topological insulators. Intrinsic magnetic topological insulators are …
Applying ‘magic angle’ twistronics to manipulate the flow of light
‘Twisted’ layers of 2D materials produce photonic topological transition at ‘magic’ rotation angles Principles of Moire-pattern bilayer graphene applied to 2D material photonics for first time Monash researchers are part of an international collaboration applying ‘twistronics’ concepts (the science of layering and twisting 2D materials to control their electrical properties) to manipulate the flow of light in extreme ways. The …