- High exciton-polariton density in an engineered quantum box
- Possible pathway to future, ultra energy-efficient technologies

FLEET/ANU’s Dr Matthias Wurdack in the lab at the Australian National University (Credit: Phil Dooley ANU)
Australian researchers have engineered a quantum box for polaritons in a two-dimensional material, achieving large polariton densities and a partially ‘coherent’ quantum state.
New insights coming from the novel technique could allow researchers to access striking ‘collective’ quantum phenomena in this material family, and enable ultra-energy efficient and high-performant future technologies.
The key to the construction of the quantum box was the use of a ‘small’ 2D material (tungsten disulphate) on top of a ‘large’ heterostructure containing the same material. This allowed the researchers to carefully investigate and compare the properties of the polaritons trapped in the box and of freely moving polaritons.
“We have been able to demonstrate that polaritons which form anywhere outside the quantum box can travel for many micrometres and be trapped and accumulate inside the box”, explained lead researcher Dr Matthias Wurdack (Australian National University).
Why we need large polariton densities
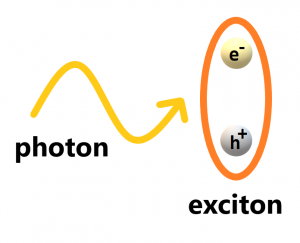
Exciton polariton: a hybrid particle composed of a photon (light) and an exciton (a bound electron-hole pair)
Exciton-polaritons are a promising platform for future ultra-low energy electronics, because they can flow without any wasted dissipation of energy, in a fully ‘coherent’ quantum state.
Novel, 2D, atomically-thin semiconductors (TMDCs) are promising candidates for such future technologies because excitons are stable in these materials at room temperature.
(Room temperature operation is important in any viable, alternative low-energy technology, so that the energy required to supercool the device does not outweigh the gains.)
“However, this ‘dissipationless’ transport requires a phase transition to a macroscopically coherent quantum state, which only occurs at very large particle densities that are hard to access in 2D semiconductors”, explains group leader Prof Elena Ostrovskaya (also at the ANU).
“The new technique allows ANU researchers to create high polariton densities in an engineered ‘quantum box’.”
Exciton polaritons: a short explainer
An ‘Exciton’ is a bound electron-hole pair and can be created in a direct bandgap semiconductor, where a photoexcited electron in the conduction band binds to a positively charged electron-vacancy (hole) in the valence band.
Mixing these excitons with light leads to the formation of the sought-after, hybrid light-matter particles called ‘exciton-polaritons’, which can travel through the semiconductor without dissipating energy in heat.
The ‘mixing’ is accomplished by placing a 2D semiconductor inside a microcavity consisting of two mirrors, separated by a few hundred nanometers, which confines light.
In such a device, the excitons in the 2D semiconductor can strongly couple to the confined light, forming exciton-polaritons (often referred to as just ‘polaritons’).
How to build a quantum box
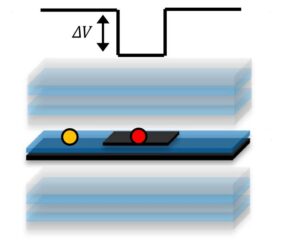
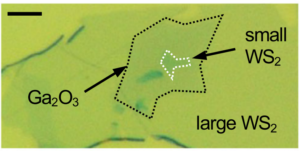
The key to the construction of the quantum box was the placement of a ‘small’ 2D material on top of a ‘larger’ layer, creating a potential well within the boundaries of the smaller layer**
In the microcavity/heterostructure device, exciton-polaritons interacting with each other can undergo a phase transition to the dissipationless quantum state of Bose Einstein condensate (BEC) or superfluid, which could be utilized in future technologies.
This phase transition can be achieved at room temperature at sufficiently large particle densities.
A popular method to increase particle density, and hence the interactions of polaritons, is to spatially confine them inside a quantum box.
However, building a quantum box for exciton polaritons in 2D materials is difficult, because these materials are extremely fragile and easily damaged using conventional nanofabrication techniques.
The FLEET/ANU researchers found a new way to build such a quantum box mechanically, without the need of nanofabrication machines that expose the fragile 2D materials to hot and abrasive particles.
This was done by placing a ‘small’ monolayer of the TMDC tungsten disulfide (WS2), on top of a ‘large’ WS2 monolayer spaced by ultrathin Ga2O3 glass, inside the mirrored microcavity.
The ‘small’ and ‘large’ sizes are relative to the particle wavelength of an exciton-polariton.
The smaller layer creates a ‘potential well’ because within its boundaries there is a stronger coupling of the exciton to light, which robs polaritons of potential energy, so that now they don’t have enough energy to escape the well.
The construction allows researchers to accumulate and confine polaritons within the ‘box’ trap formed by the potential well, thus greatly increasing polariton density within the box.
Study confirms a step towards desired quantum state
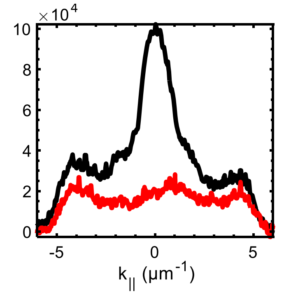
Researchers were able to compare polariton characteristics both inside and outside the box trap.
They found that the trapping leads to energy redistribution towards lower energy states, signalling an advance towards the desired quantum states of BEC and superfluidity.
Additionally, the researchers found that trapping significantly enhances the macroscopic coherence of the polaritons, even before the BEC phase is reached.
This is because the confined light is much longer lived than the WS2 excitons, and trapping strongly reduces the phase fluctuations of the polariton gas.
Remarkably, the enhanced coherence in the trap was also achieved when the polaritons were exclusively created outside of the trapping region and populated the trap by traveling towards it across the sample.
Novel materials
The semiconductors used in this study belong to the family of transition metal dichalcogenide crystals (TMDCs), which are layered crystals that are weakly bound via van-der-Waals interactions (similar to the graphite in pencils).
Because the bonds between layers are so weak, researchers can ‘thin out’ these crystals relatively simply using the ‘Scotch tape’ method – first, famously, used by Geim and Novoselov to isolate 2D graphene in 2010.
When thinned out to the monolayer limit (ie, one atom thin), light at a distinct wavelength strongly interacts with the monolayers, directly creating excitons. (This process does not occur in the bulk crystals.)
2D TMDCs are considered promising platforms for future technology because excitons in these materials are stable at room temperature.
However, excitons in TMDCs possess only weak effective interactions with each other, making ‘collective’ quantum phenomena such as BEC and superfluidity hard to reach.
“While the excitons in TMDCs interact strongly with light to form exciton-polaritons, the exciton-polaritons in TMDCs interact only weakly with each other,” explains Matthias. “A very high polariton density could be a way around this challenge”.
The study
Enhancing ground-state population and macroscopic coherence of room-temperature WS2 polaritons through engineered confinement was published in Physical Review Letters in October 2022 (DOI 10.1103/physrevlett.129.147402)
Funding was received from Australian Research Council (Centres of Excellence and DECRA programs), and from the European Research Council.
More information
- Contact Dr Matthias Wurdack (Australian National University) matthias.wurdack@anu.edu.au
- Contact Prof Elena Ostrovskaya (Australian National University) elena.ostrovskaya@anu.edu.au
** images from Physical Review Letters